Pandas Dataframe: Union and Concat Examples
Last updated:Table of Contents
Pandas version 1.x used
Union all
The default behaviour for
concatis not to remove duplicates!
Use pd.concat([df1, df2], ignore_index=True) to make sure sure the index gets reset in the new dataframe.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'name':['john','mary'],
'age':[24,45]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'name':['mary','john'],
'age':[45,89]
})
# pass dataframes as a list
pd.concat([df1,df2], ignore_index=True)
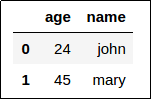 Dataframe 1
Dataframe 1
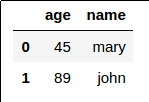 Dataframe 2
Dataframe 2
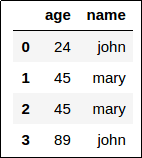 Union of Dataframe 1 and 2:
Union of Dataframe 1 and 2: (The index was reset and
the duplicate row was NOT removed
Union
In SQL, the union keyword implies that duplicates are removed:
To remove duplicates, use drop_duplicates().reset_index(drop=True) at the end.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'name':['john','mary'],
'age':[24,45]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'name':['mary','john'],
'age':[45,89]
})
pd.concat([
df1,df2
],ignore_index=True).drop_duplicates().reset_index(drop=True)
 Dataframe 1
Dataframe 1
 Dataframe 2
Dataframe 2
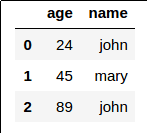 Union of Dataframe 1 and 2:
Union of Dataframe 1 and 2: No duplicates now
Concat horizontally
To concatente dataframes horizontally (i.e. side-by-side) use pd.concat() with axis=1:
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'name':['john','mary'],
'age':[24,45]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'name':['mary','john'],
'age':[45,89]
})
pd.concat([
df1,df2
],axis=1)
 Dataframe 1
Dataframe 1
 Dataframe 2
Dataframe 2
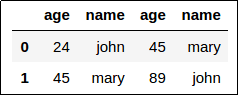 Concatenation of Dataframe 1 and 2:
Concatenation of Dataframe 1 and 2: Pandas will not warn you if you try
to concatenate two dataframes that have
columns with the same name!
Concat vertically
This is the same as applying SQL Union All