Set up Heartbeat Monitoring on AWS Cloudwatch with Boto: Example
Last updated:
AWS Credentials needed you need to have AWS credentials to do this (
ACCESS_KEY_IDandSECRET_ACCESS_KEYin~/.aws/credentials)Full code available on this jupyter notebook
Install boto
$ pip install boto3
Put custom metric
You don't need to create the metric beforehand. The first time you put a value it'll be automatically created for you.
Use this code to send a custom metric to cloudwatch. This will be used as a heartbeat later on.
import boto3
# If you get errors at this point, check your credentials files
# under ~/.aws/credentials
cloudwatch_client = boto3.client('cloudwatch')
cloudwatch_client.put_metric_data(
MetricData = [
{
'MetricName': 'heartbeat',
'Unit': 'None',
'Value': 42, # must be a number
'Dimensions': [
{
'Name': 'feature-name',
'Value': 'my-feature-1'
}
]
}
],
Namespace='my-app-1'
)
Check metric on Cloudwatch
Make sure you look at the console in the correct region
Once you call the code above at least once, the metric will be available for you to check on the cloudwatch console:
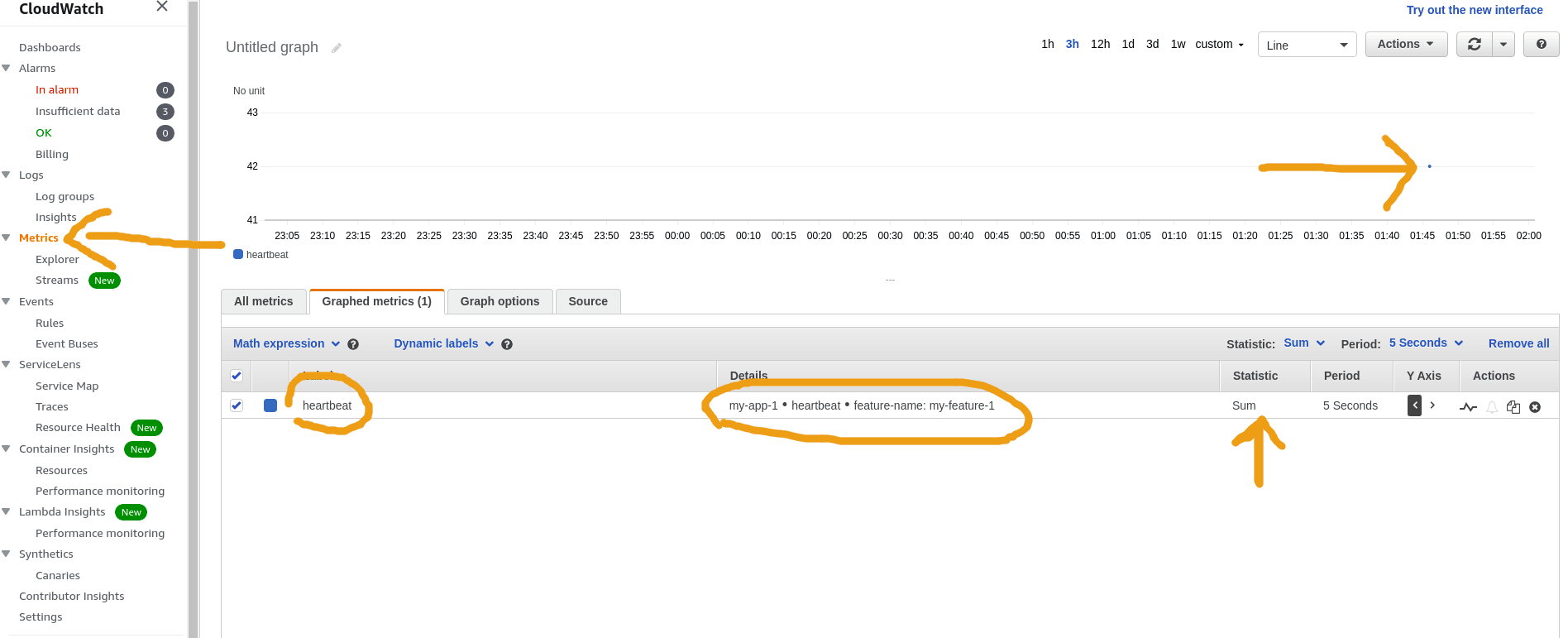 Click on Metrics on the left and select
Click on Metrics on the left and select the metric you have just put and you
will see a point in the graph
Setup alarm
The alarm will be used to check if the heartbeat has not been sent.
In this example, we will get notified if not heartbeat has been sent for 6 hours:
1) Click the bell button on the right to setup the alarm
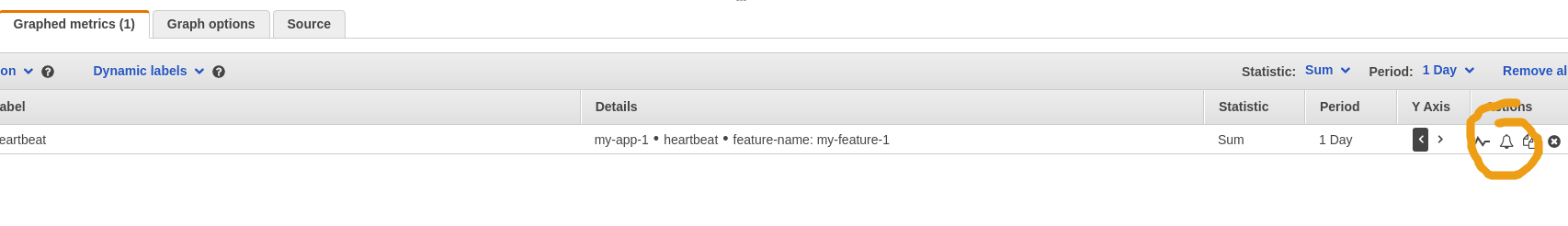 Click the bell button to open
Click the bell button to open
the alarm setup screen2) Set condition that will never be met
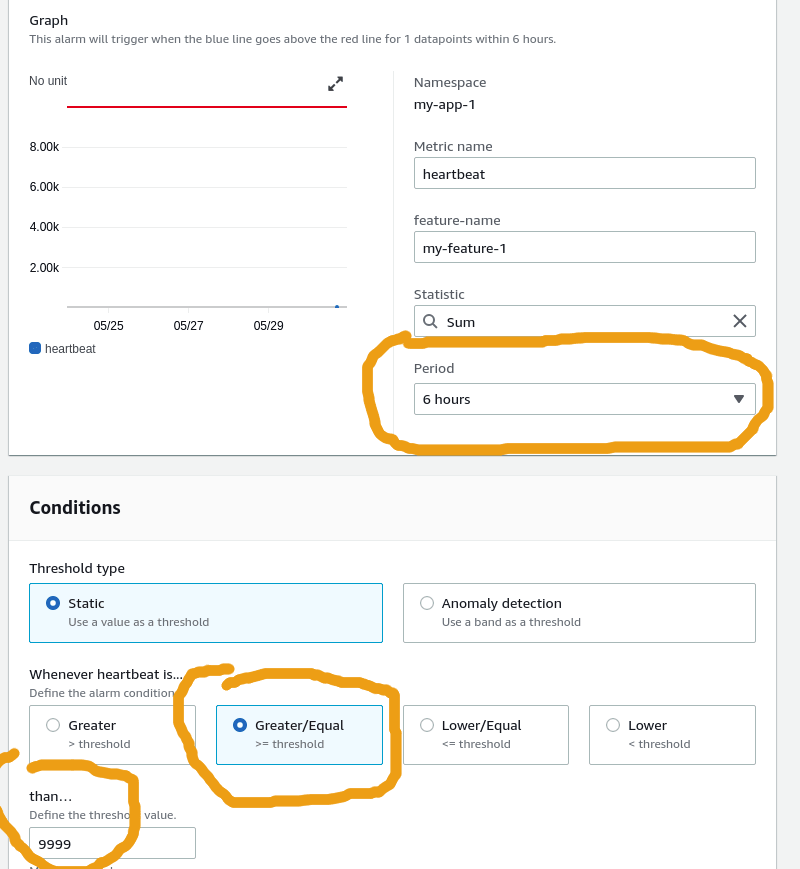 As an example, set an alarm that you know will never be triggered.
As an example, set an alarm that you know will never be triggered.
We do this because we want to check for missing data instead.3) Open "Additional Configuration" and choose "Treat missing data as bad (breaching threshold)"
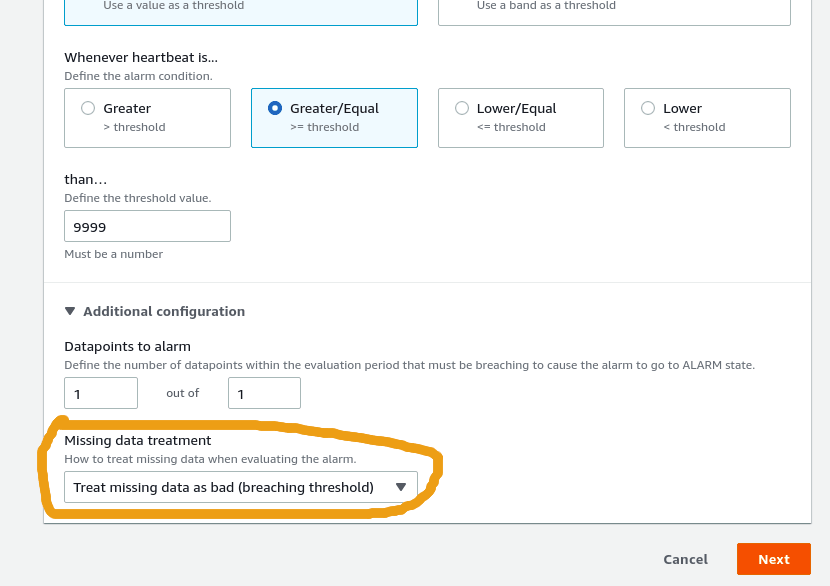 By setting this option, the alarm will go off when
By setting this option, the alarm will go off when
the metric doesn't get any data,
which is what we want.4) Click next, choose final details and click "Create Alarm"
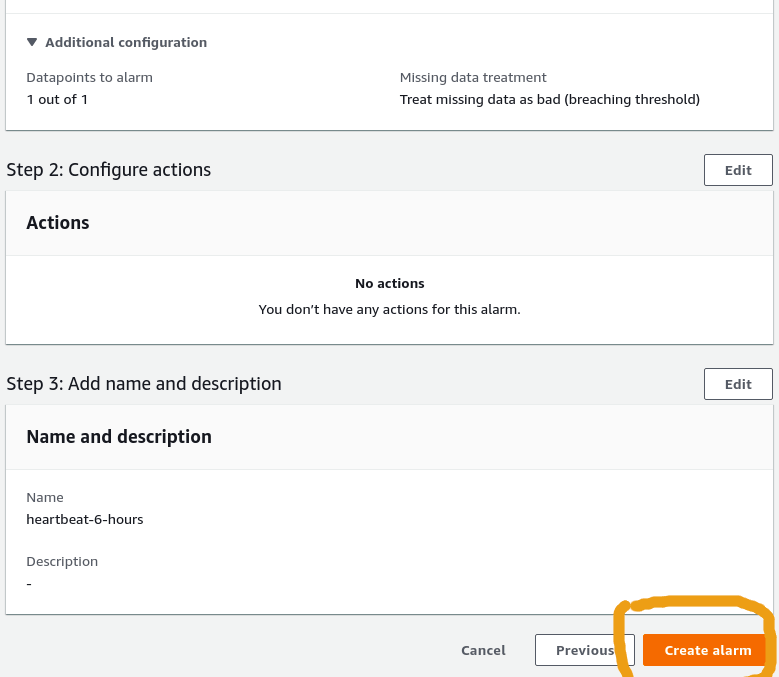 Create alarm, final step
Create alarm, final step
Check alarm condition
Once the alarm is setup, you will be notified if there are no heartbeats sent for 6 hours:
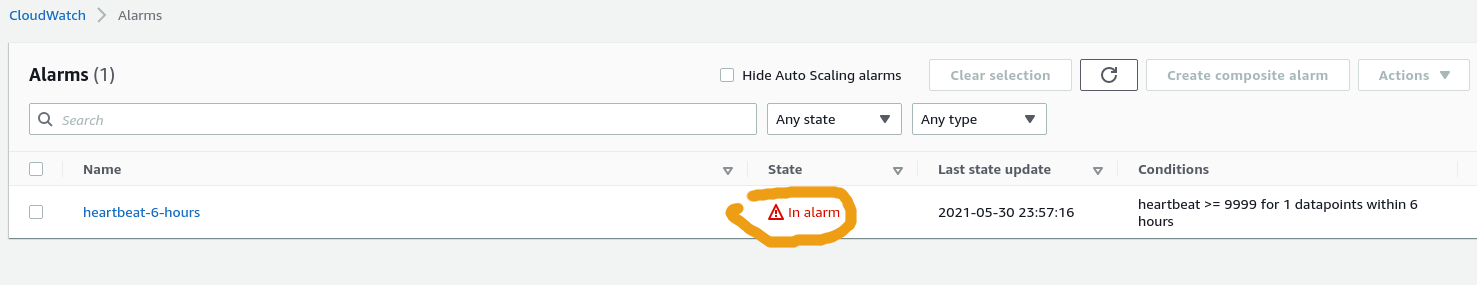 This is what it looks like when there weren't
This is what it looks like when there weren't heartbeats for the last 6 hours
 Click the bell button to open
Click the bell button to open  As an example, set an alarm that you know will never be triggered.
As an example, set an alarm that you know will never be triggered.  By setting this option, the alarm will go off when
By setting this option, the alarm will go off when  Create alarm, final step
Create alarm, final step